Keywordsbrand loyalty brand trust perceived value service quality
JEL Classification M31
Full Article
1. Introduction
Research on brand loyalty had been widely conducted in a variety of contexts including in the mobile phone industry, particularly in measuring the determinants of brand loyalty of pre-paid products. Indonesia has great market potential for the mobile phone industry, but a very intense competition has developed recently. The high level of penetration of mobile phone market in Indonesia makes the number of mobile phone players in this industry interested to take a part in achieving a higher market share in Indonesia (Ningsih, 2014).
Indonesia currently has eight telecommunication operators that serve the needs of approximately 257.9 million people. Five of them are based on Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM). They are PT Telekomunikasi Seluler (Telkomsel), PT Indosat Tbk (ISAT), PT XL Axiata (EXCL), PT Smartfren Telecom Tbk (FREN), and PT Hutchison CP Telecommunication. Besides, four of them are based on Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) that consist of PT Bakrie Telekom Tbk (BTEL)/Mobile-8, PT Sampoerna Telekomunikasi Indonesia (STI), and Natrindo Telepon Indonesia/PT Axis Telekom Indonesia (Ditjen SDPPI, 2014 and Anestia, 2015). Statistically, the growth of cellular phones since 2004 reached 29,836,607 customers and continued to grow to 358,130,675 customers, in 2015. The evolution of cellular customers in Indonesia from 2004 to 2015 can be seen in Figure 1.
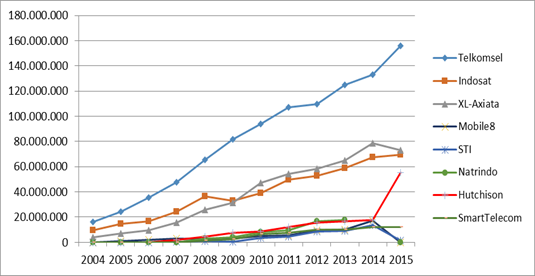
Figure 1. Mobile Phone Customers Growth from 2004 to 2015
Source: Ditjen SDPPI, (2015)
The high growth of mobile phone customers in Indonesia could encourage a higher mobile phone market share that could make Indonesia as an important potential area for the telecommunications market. The trend of positive growth to all mobile phone operators has caused little changes in the market share of each operator in recent years. Telkomsel, Indosat, and XL-Axiata are the three operators with the largest share of customers in Indonesia. The customer is the important unit in telecommunication services which is operating in a competitive brand environment where telecommunication brand service providers need to be aware of the various factors boosting brand loyalty in order to build effective business strategies for customers’ retention (Lim et al., 2006).
Attention to the determinants of brand loyalty through perceived value, service quality, and satisfaction have also been used to measure the significance of the relationship between brand loyalty and its determinants. Deng et al., (2010) Ishaq et al., (2014, 2015) and Osman et al. (2016) conclude that the observed variables can be used, or not, in measuring brand loyalty, therefore, debates and inconsistencies occur in marketing literature.
2. Theoretical Review of Brand Loyalty
The study of brand loyalty has been widely conducted in various areas and contexts, including in the mobile phone industry. To measure brand loyalty, previous researchers used various variables as determinants of brand loyalty, such as perceived value (Rasheed and Timeless, 2014; Chang, 2015; Yeh et al., 2016), service quality (Hou and Wonglorsaichon, 2011; Hafeez and Muhammad, 2012; Rasheed and Abadi, 2014), customer satisfaction (Chang, 2015, Asiamah et al., 2016; Hew et al., 2016), and brand trust (Hou and Wonglorsaichon, 2011; Liao, 2015).
The researchers also prove that a customer’s loyalty to a brand is also conducted through costumer brand identification, brand trust, and word of mouth communication (Nikhashemi et al., 2015). Furthermore, (Chang, 2015 and Yeh et al., 2016) says that value perception through the dimensions of emotional value, social value, price value, and quality value can increase the brand loyalty for a service. While Dehghan et al. (2015) say that the dimensions of utilitarian value, hedonistic value, value perception, customer satisfaction and customer value can measure the customer loyalty for a brand. Park and Kim (2016) state that brand loyalty can be measured through dimensions of brand value, brand trust, and brand effects. Further, Hou and Wonglorsaichon (2011) and Lam and Shankar (2014) use dimensions of value perception, brand satisfaction, trust, and brand attachment to enhance brand loyalty.
3. The Relationship between Loyalty and its Determinants
Referring to the problems of the mobile phone industry in Indonesia, the relationship framework of the determinants of brand loyalty measured by value perceptions, service quality, brand trust through the study of various previous researches literature is structured as follows in the two sub-sections, namely the relationship between customer value and brand loyalty, and the relationship between service quality and brand loyalty.
3.1.The Relationship between Customer Value and Brand Loyalty
Value perception is the value of a product that is expected and perceived by the consumer. The expectation of a costumer regarding a product is different than for other consumers, in terms of purchase quantity, service quality, convenience (before purchase, using and after purchasing) and so on. Krisnanto (2017) mentions that the value of the customer is the source of all value in the organization, and creating strong customer value is the main goal of every company.
From the perspective of the customer, Chuah et al. (2014) state that the value model that is oriented on the customer is based on the functional value, monetary value, emotional value, adjustment value, and relational values, which are the predictors that can be used to influence various aspects of customer loyalty to brands (behavioral attitudes and composites). Ishaq (2012) reports that the value perception is proven and able to build the customer loyalty to the brand in the telecommunications industry. The value perception also affects the customer in consuming the brand, directly, and can also cause the customer loyalty to the brand, indirectly (Wongsuchat and Ngamyan, 2014).
In addition, Rasheed and Abadi (2014) say that service quality, trust, and value perceptions are antecedents of loyalty where they find that service quality, trust, and perception value factors have a positive relationship with brand loyalty. Value perception consists of the emotional value, social value, price value for money and performance/quality value have a relationship with brand loyalty (Chang, 2015; Chua et al., 2015). Some surveys support the loyalty model as a function of expressive response and instrumental customer that result in trust of costumer on the brand intrinsically or extrinsically and heuristics and rational values based on perceived value.
Meanwhile, Lam and Shankar (2014) report that in the early adoption type of inter-generation adopters of the equipment telecommunication technology is influenced by the perceived brand value. Furthermore, (Deghan et al.) 2015; Yeh et al. (2016) find that perceived values that include functional value, emotional value, social value, and brand identification have a positive effect on brand loyalty for mobile phones in Taiwan. In line with previous researchers, Nikhasemi et al. (2016) and Rahmani et al. (2017) conclude that the creation of customer value would have an effect on the high loyalty of customers in consuming telecommunication brands.
3.2.The Relationship between Service Quality and Brand Loyalty
Nowadays, the concept and measurement of service quality have experienced a rapid grown in research. Krisnanto (2017) claims that service quality has an accurate capability to meet the needs of a service, willingness to help customers, knowledge, and friendliness of employee, and personal attention to customers, as well as the provision of physical facilities and overall employee appearances. According to Parasuraman, Zeithaml and Berry (1985), the main contributor to the measurement of service quality is presented in five dimensions, namely:
1. Reliability is the ability to deliver promised services immediately, accurately and satisfactorily.
2. Responsiveness is the desire of the staff to help the customers and provide services with responsiveness.
3. Warranties which include knowledge, competence, courtesy and credentials of staff, free of danger, risk or doubt.
4. The empathy that consists of simplicity in making relationships, good communication, personal attention, and understanding the needs of consumers.
5. Direct evidence which includes physical facilities, equipment, employees, and means of communication.
According to Akbar et al. (2010), the quality of service has a positive influence on loyalty. Furthermore, Zehir et al. (2011) say that the quality of service and perception of brand communications affect brand trust which will ultimately affect brand loyalty either directly or indirectly.
Further, Hafeez and Muhammad (2012) and Ishaq (2012) conclude that service quality, customer satisfaction, and loyalty programs are important factors that can increase customer loyalty to the brand. Rasheed and Abadi (2014) say that service quality is the antecedent of customer loyalty to the brand. But it is unlike with the previous opinions stated by Hou and Wonglorsaichon (2011), that the perception of the perceived quality of consumers will negatively affect brand loyalty.
3.3. The Relationship between Brand Trust and Brand Loyalty
Hasan et al. (2014) say that trust along with the believed values has a long-term relationship with the brand. The belief in the brand will ultimately lead the customers to their commitment and loyalty to the brand. In addition, the brand must also be able to increase the customers emotional involvement so that the customers have a bond and loyal to the brand (Barusman, 2016).
The first dimension of trust is known as cognitive-based beliefs, knowledge-based beliefs, or system beliefs (Lewicky and Stevenson, 1997). While Hou and Wonglorsaichon (2011) state that brand trust has a positive effect on loyalty, Zur et al. (2012) report that the type of perceived belief is objective and it is based on a rational process that determines whether the other parties in the relationship can be trusted.
The second dimension of trust is known as the trust-based influence, emotional trust, interpersonal trust, or relational trust (Guenzi and Georges, 2010). The perceived type of belief is subjective naturally and based on feelings, emotions, and other moods (Zur et al., 2012). Further, Ahmed (2014) and Liao (2015) say that brand trust still becomes a positive determinant of brand loyalty.
4. Theoretical Framework
The theoretical framework proposed in this research is presented in Figure 2.
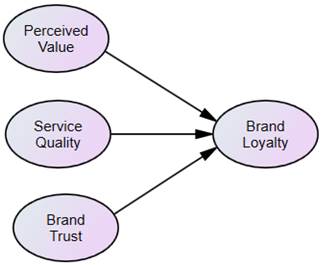
Figure 2. Theoretical Framework
5. Research Methodology
This research is conducted on the customers of mobile phone in Aceh Province and analyzed using Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) techniques which is operated through the Analysis of Moment Structure (AMOS) program.
6. Conclusion
6.1. Theoretical Contribution
The objectives of this literature study are to identify the dimensions of the value perception, service quality, and brand trust of customers in the telecommunications industry and to examine the relationship between value perception, service quality, and brand trust toward brand loyalty in the telecommunication industry. This research also provides value enrichment which arises from the model submission of brand loyalty of customers in further studies with different perspectives and dimensions.
In terms of practical contribution, if this conceptual framework were empirically tested, it can provide valuable insight to marketing practitioners in formulating customer-oriented marketing strategies. This framework will also assist marketing practices in creating competitive advantages in telecommunications industry which will ultimately create customer loyalty to the brand.
6.1. Suggestions for Further Researches
Brand loyalty is an important concept in improving sustainable income. The concept of brand loyalty has evolved in various business dimensions as a customer retention strategy for businesses where the loyal customers will always make frequentative purchases when the needs and desires arise. In a competitive business telecommunication service context, brand loyalty is an absolute necessity.
This study examines the effect of perceived value, service quality and brand trust on brand loyalty in the mobile phone industry. Future researchers are expected to test the concept of brand loyalty through other concepts, such as brand commitment (Fullerton, 2005), customer credibility (Bachri, et al., 2016), brand experience (Wulandari, 2016), and Brand Attachment (Chinomona, 2013).
References
- Ahmed, Z., 2014. Effect of brand trust and customer satisfaction on brand loyalty in Bahawalpur. Journal of Sociological Research, 5(1), pp.306-326.
- Akbar, S., Som, A.P.M., Wadood, F., and Alzaidiyeen, N.J. 2010. Revitalization of Service Quality to Gain Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty. International Journal of Business and Management, 5(6), pp.113-122.
- Anestia, C., 2015. Pertumbuhan Pelanggan Seluler. Jakarta: Indonesian Finance Today.
- Asiamah, E.Y., Nimako, S.G., Quaye, D.M., and Buame, S., 2016. Implicit and explicit: the role of satisfaction, trust and brand image in mobile telecommunication industry. International Journal Business and Emerging Markets, 8(1), pp.94-115.
- Bachri, N., Lubis, A.R., Nurdasila, and Majid, M.S.A., 2016. Credibility and consumer behavior of Islamic bank in Indonesia: A literature review. Expert Journal of Marketing, 4(1), pp.20-23.
- Barusman, A.R.P., Riorini, S.V., 2016. Zone-of-Tolerance moderates satisfaction customer trust and inertia-customer loyalty. IJABER, 14(16), pp.4847-4865.
- Chang, C.C., 2015. Exploring mobile application customer loyalty: The moderating effect of use contexts. Telecomunication Policy, 39, pp.678-690.
- Chinomona, R., 2013. The influence of brand experience on brand satisfaction, trust and attachment in South Africa. International Business and Economics Research Journal, 12(10), pp.1303-1316.
- Chua, B.L., Lee, S., Goh, B., and Han, nH., 2015. Impact of cruise service quality and price on vacationers’ cruise experience: Moderating role of price sensitivity. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 44, pp.131-145.
- Chuah, H.W., Marimutu, M., and Ramayah, T., 2014. The effect of perceived value on the loyalty of generation Y mobile internet subscribers: A proposed conceptual frame work. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 130, pp.532-541.
- Dehghan, N.A., Alizadeh, H., and Alamouti, S.M., 2015. Exploring the customer perceived values as antecedent of purchase behavior. Serbian Journal of Management, 10(2), pp.173-188.
- Deng, Z., Lu, Y., Wei, KK., and Zhang, J., 2010. Understanding Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty: An empirical study of mobile instant messages in China. International Journal of Information Management, 30, pp.289-300.
- Direktorat Jenderal Sumberdaya Manusia dan Perangkat Pos dan Informatika, 2015. Data Statistik pertumbuhan pengguna telepon seluler Indonesia.
- Fullerton, G., 2015. The impact of brand commitment on loyalty to retail service brand. Canadian Journal of Administrative Sciences, 22(2), pp. 97-110.
- Guenzi, P. and Georges, L., 2010. Interpersonal trust in commercial relationship. Antecedents and consequences of customer trust in the salesperson. European Journal of Marketing, 44(1-2), pp.114-138.
- Hafezz, S. and Muhammad, B., 2012. The impact of service quality, customer satisfaction and loyalty program on customer loyalty: Evidence from Banking sector of Pakistan. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 3(16), pp.200-209.
- Hasan, H., Kiong, T. and Ainuddin, R.A., 2014. Effects of perceived value and trust on customer loyalty towards foreign Bank in Sabah, Malaysia. Global Journal of Emerging trends in e-Business, Marketing and consumer psychology (GJETeMCP) An Online International Research Journal, 1(2), pp.137-153.
- Hew, J.J., Lee, V.H. and Ooi, K.B., 2016. Mobile social commerce: The booster for brand loyalty. Computer in Human Behavior, 59, pp.142-154.
- Hou, C. and Wonglorsaichon, P., 2011. The relationship among brand awareness, brand image, perceived quality, brand trust, brand loyalty, and brand equity of customer in China’s antivirus software industry. International Journal of Business and Economics, 8(1), pp.151-171.
- Ishaq, M.I., 2012. Perceived value, service quality, corporate image, and customer loyalty: Empirical assesment from Pakistan. Serbian Journal of Management, 7(1), pp. 25-36.
- Ishaq, M.I., Bhutta, M.H., Hamayu, A.A., Danish, R.Q. and Husain, N.H., 2014. Role of corporate image, product quality, and customer value in customer loyalty: Intervening effect of customer satisfaction. Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research, 4(4), pp.89-97.
- Krisnanto, U., 2017. Empirical study on the relationships of internet banking quality, customer value, and customer satisfaction. Expert Journal of Marketing, 5(1), pp.17-27.
- Lai, I.K.W., 2015. The role of value, satisfaction, and commitment in the effect of service quality on customer loyalty in Hongkong-Style tea restaurant. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly, 56(1), pp.118-138.
- Lam, S.Y. and Shankar, V., 2014. Asymmetries in the effects of drivers of brand loyalty between early and late adopters and across technology generations. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 28, pp.26-42.
- Lewicki, R.J., and Stevenson, M.A., 1997. Trust development in negotiation: proposed actions and a research agenda. Business and Professional Ethics Journal, 16(1-3), pp.99-132.
- Liao, Y.K., 2015. The role of trust on brand loyalty and brand equity: Managing intellectual capital and innovation for sustainable and inclusive society. Management, Knowledge, and Learning, Joint International Conference, 27-29, May 2015.
- Lim, H., Widdows, R. and Park, F., 2006. M-loyalty: Winning strategies for mobile carriers. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 23(4), pp.208-218.
- Nikhashemi, S.R., Tarofder, A.K., Baur, S.S. and Haque, A., 2016. The effect of customer’s perceiced value of retail store on relationship between store atribute and customer brand loyalty: Some insight from Malaysia. Procedia Economics and Finance, 37, pp.432-438.
- Ningsih, S.M. and Segoro, W., 2014. The influence of customer satisfaction, switching cost and trusts in a brand on customer loyalty-the survey on student as im3 user in Depok, Indonesia. Procedia-Social and Behavioral science, 143, pp. 1015-1019.
- Osman, Z., Mohamad, R.K., and Mohamad, L., 2016. Mediating effect of customer satisfaction on service qualityand trust relationship in Malaysian Banking Industry. International Journal of Advances in Management, Economic and Entrepreneurship, 3, Issue 1, pp.10-19.
- Parasuraman, A., Zeithaml, V.A. and Berry, L.L., 1985. A conceptual model of service quality and its implications for future research. Journal of Marketing, 49, pp.41-50.
- Park, H. and Kim, Y.K., 2016. Proactive versus reactive apparel brands in sustainability: Influences on brand loyalty. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 29, pp.114-122.
- Rahmani, Z., Rajbar, M., Nadigara, A.A. and Gorji, M.A.H., 2017. The study of the relationship between value creation and customer loyalty with the role of trust moderation and customer satisfaction in Sari Hospital. Electronik Physian Excellence in Constructive Peer Review, 9(6), pp.4474-4478.
- Rasheed, F.A. and Abadi, M.F., 2014. Impact of service quality, trust and perceived value on customer loyalty in Malaysia service industries. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 164, pp.298-304.
- Wongsuchat, P., and Ngamyan, A., 2014. A study of relations among perceived consumption value and customer satisfaction of boutique hotel in Thailand. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, 4(7), pp.1-7.
- Wulandari, N., 2016. Brand experience in banking industry: Direct and indirect relationship to loyalty. Expert Journal of Marketing, 4(1), pp.1-9.
- Yeh, C.H., Wang, Y.S. and Yieh, K., 2016. Predicting smartphone brand loyalty: consumer value and consumer-brand identification perspective. International Journal of information Management, 36, pp.245-257.
- Zehir, C., Sahin, A., Kitapci, H. and Ozsahin, M., 2011. The effects of brand communication and service quality in building brand loyalty through brand trust: The empirical research on global brands. Procedia Social and behavioral sciences, 24, pp.1218-1231.
- Zur, A., Leckie, C. and Webster, C.M., 2012. Cognitive and affective trust between Australian exports and their overseas buyers. Australian Marketing Journal, 20, pp. 73-79.
Article Rights and License
© 2017 The Authors. Published by Sprint Investify. ISSN 2359-7712. This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


